
Apr 17, 2022
0 Comment by ViewersJava is perhaps the most used programming language for developing web apps and platforms. The developers designed it to be adaptable, allowing them to build code for any machine, independent of architecture or platform. According to the Java landing page, more than 1 billion PCs and 3 billion cell phones globally use the popular programming language Java.
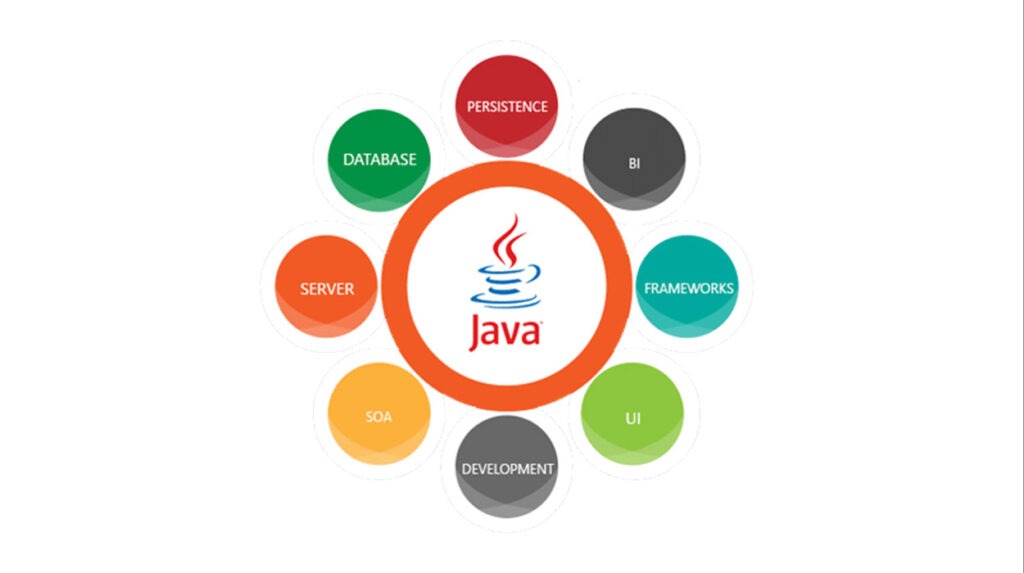
Java is used to construct applications and platforms for a number of devices, including computers, laptops, gaming consoles, Blu-ray players, car navigation systems, medical monitoring devices, parking meters, lottery terminals, and smartphones. It is additionally a key language for networking, especially for data centers that store and transfer Web-based data.
Additionally, Web pages can run alongside or embed miniature, dynamic programs created with Java. Web pages can display maps, weather, games, and other interactive widgets or tools through these programs, known as applets.
In view of a C and C++-based syntax, Java is object-oriented and class-based. Developers choose and utilize Java due to its ability to securely execute code on almost any platform, irrespective of the operating system or device architecture, provided the device has the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installed. The JRE varies depending on the specific type of device, but basically it runs a “virtual” machine, or environment, that translates the code into an application or program.
Despite the fact that their names are quite similar and they are both used to create dynamic tools and games on a Web page, Java and JavaScript are different languages. Java is more powerful and can be utilized as the sole programming language for an application, while JavaScript is a lightweight scripting language that adds functionality—like a Java applet—to a Web page.
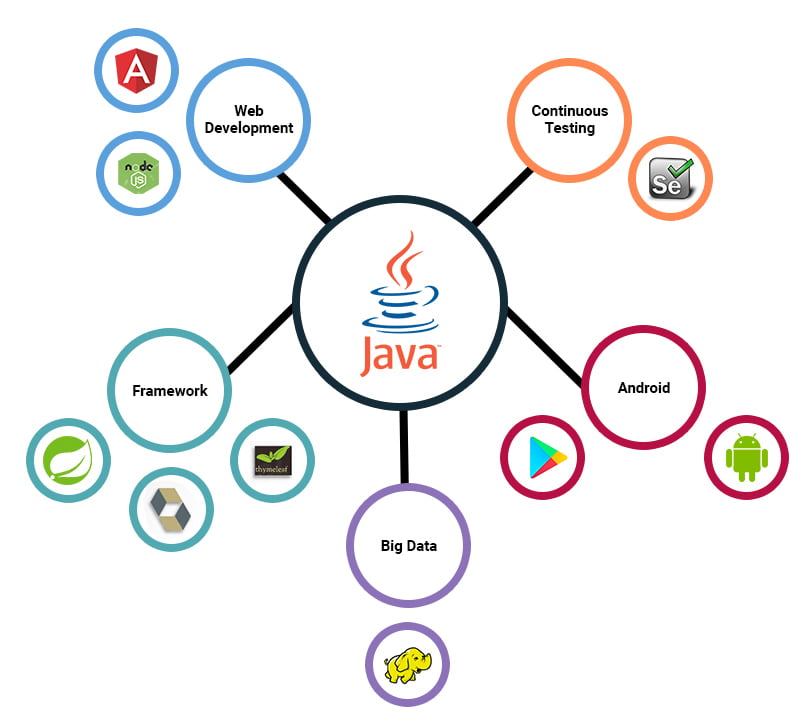
The answer lies primarily in the thorough testing, updating, and consistency of delivery that Java has historically provided. A dedicated community of Java developers, architects, and enthusiasts has tested, refined, extended, and proven Java. Despite having roots dating back almost two decades, Java has consistently evolved over the years.
Java, a popular language, enables the development of portable, high-performance applications for a wide range of computing platforms, thereby enabling the fundamental tenets of overarching accessibility and cross-platform interaction. By making applications available across heterogeneous environments, businesses can provide more services, boost end-user productivity, communication, and collaboration, and dramatically reduce the ownership cost of enterprise and consumer applications.
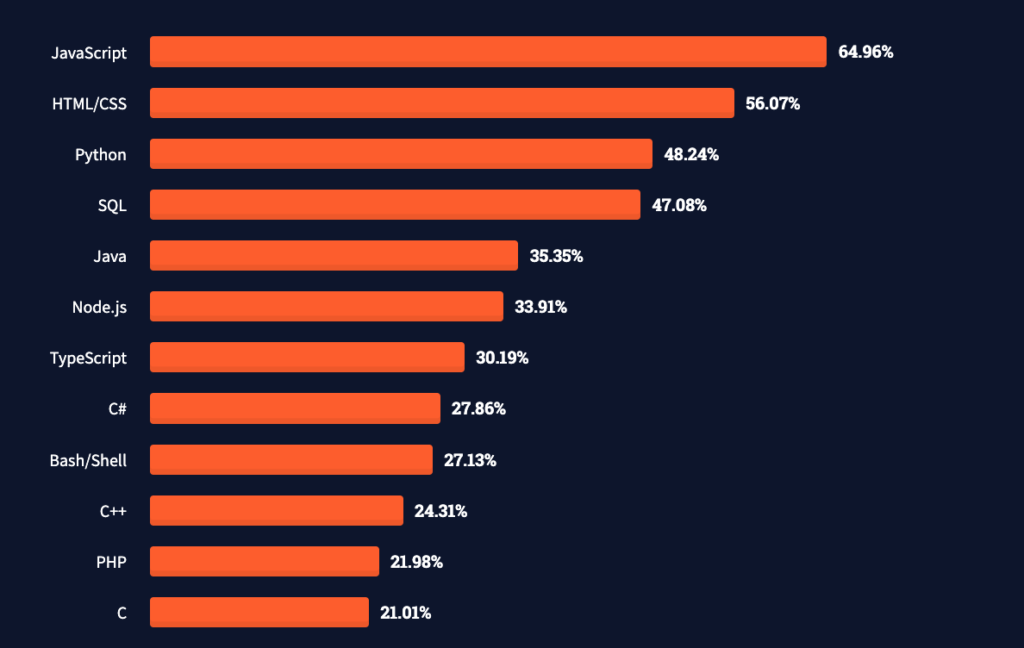
While the world of technology is continually progressing at what seems like a faster-than-ever pace, people, even coders, have an unfortunate tendency to forget about the origins—the underlying principles. These concepts have greatly impacted the development of contemporary technology. This is why Java is important—because not only does it continue to be a vital and invaluable programming language today, but it has also shaped the manner in which technology will unfold in the coming two decades and continue to unfold for the unforeseeable future.